Different types of vegetarian diets offer a spectrum of plant-based options, each with its own unique set of nutritional implications and ethical considerations. From lacto-vegetarianism to veganism, this comprehensive guide delves into the nuances of these diets, empowering readers to make informed choices that align with their health, environmental, and ethical values.
Vegetarian diets have gained increasing popularity due to their potential health benefits, reduced environmental impact, and ethical implications. Understanding the various types of vegetarian diets is crucial for individuals considering adopting a plant-based lifestyle.
Types of Vegetarian Diets
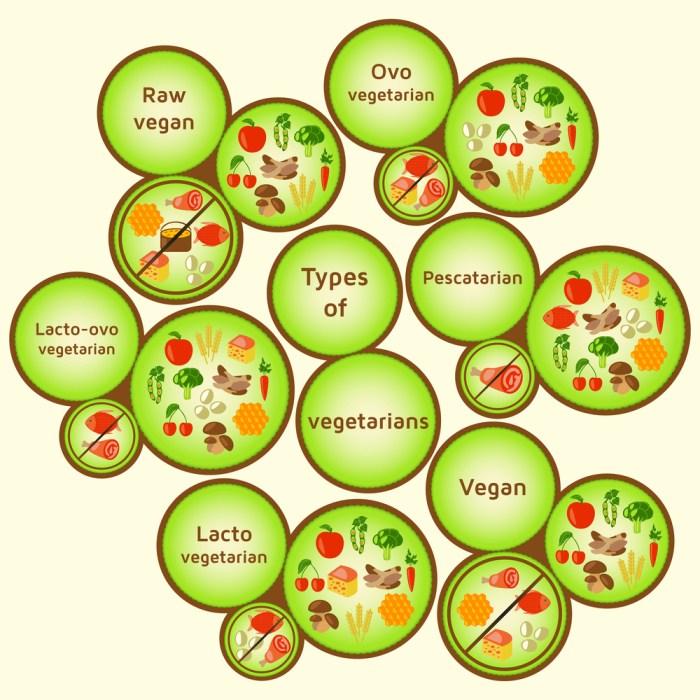
Vegetarianism is a type of diet that excludes the consumption of meat, poultry, and fish. There are several different types of vegetarian diets, each with its own set of restrictions and allowances.
The main types of vegetarian diets include:
Lacto-Vegetarian Diet
Lacto-vegetarians exclude meat, poultry, fish, and eggs from their diet but allow dairy products, such as milk, cheese, and yogurt.
- Allowed foods:Fruits, vegetables, whole grains, legumes, nuts, seeds, dairy products
- Excluded foods:Meat, poultry, fish, eggs
Nutritional Considerations
Vegetarian diets can provide all the essential nutrients for good health, but it is important to be aware of the potential nutritional implications and to take steps to ensure adequate intake of certain nutrients.
Vegetarians need to pay particular attention to their intake of protein, iron, calcium, and vitamin B12. Protein is essential for building and repairing tissues, iron is necessary for carrying oxygen throughout the body, calcium is important for bone health, and vitamin B12 is essential for the nervous system and blood cells.
Protein
Plant-based proteins are generally not as complete as animal proteins, meaning they do not contain all of the essential amino acids. However, by eating a variety of plant-based foods, vegetarians can get all the essential amino acids they need.
- Good sources of plant-based protein include beans, lentils, tofu, tempeh, nuts, and seeds.
- Vegetarians should aim to consume about 0.8 grams of protein per kilogram of body weight per day.
Iron
Iron is an essential mineral that is necessary for carrying oxygen throughout the body. Vegetarians are at risk for iron deficiency because plant-based foods contain less iron than animal-based foods.
- Good sources of plant-based iron include beans, lentils, tofu, tempeh, spinach, and fortified cereals.
- Vegetarians should aim to consume about 18 mg of iron per day.
- Vitamin C helps the body absorb iron, so it is important to eat foods rich in vitamin C, such as fruits and vegetables, with iron-rich foods.
Calcium
Calcium is an essential mineral that is necessary for bone health. Vegetarians are at risk for calcium deficiency because dairy products are a major source of calcium.
- Good sources of plant-based calcium include fortified plant milks, yogurts, and juices, leafy green vegetables, and tofu.
- Vegetarians should aim to consume about 1,000 mg of calcium per day.
Vitamin B12
Vitamin B12 is an essential vitamin that is necessary for the nervous system and blood cells. Vitamin B12 is only found in animal products, so vegetarians need to take a vitamin B12 supplement or eat fortified foods.
- Good sources of fortified foods include plant milks, yogurts, and cereals.
- Vegetarians should aim to consume about 2.4 mcg of vitamin B12 per day.
Health Benefits
Vegetarian diets have been associated with numerous health benefits, including reduced risk of chronic diseases, improved heart health, and weight management. These benefits are attributed to the high intake of fruits, vegetables, legumes, and whole grains, which are rich in fiber, antioxidants, vitamins, and minerals.
Looking for a nutritious and plant-based way to shed those extra pounds? Consider adopting a menu diet vegetarian. This wholesome approach to eating emphasizes fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and legumes, providing your body with essential vitamins, minerals, and fiber.
By incorporating a variety of plant-based foods into your meals, you’ll not only satisfy your hunger but also support your overall well-being.
Reduced Risk of Chronic Diseases, Different types of vegetarian diets
Studies have shown that vegetarians have a lower risk of developing chronic diseases such as heart disease, stroke, type 2 diabetes, and some types of cancer. The high intake of fiber in vegetarian diets helps lower cholesterol levels and improve blood sugar control, reducing the risk of heart disease and diabetes.
Additionally, the antioxidants in fruits and vegetables help protect cells from damage, which may reduce the risk of cancer.
Improved Heart Health
Vegetarian diets are typically low in saturated fat and cholesterol, which are major risk factors for heart disease. The high intake of fiber in vegetarian diets also helps lower blood pressure and improve cholesterol levels, further reducing the risk of heart disease.
Adopting a plant-based lifestyle offers numerous health benefits. If you’re considering transitioning to a vegetarian diet, exploring menu diet vegetarian can provide valuable insights into meal planning and ensuring you meet your nutritional needs.
Weight Management
Vegetarian diets are typically lower in calories and higher in fiber than non-vegetarian diets. Fiber helps promote satiety and fullness, which can lead to reduced calorie intake and weight loss. Additionally, the high intake of fruits and vegetables in vegetarian diets provides essential vitamins and minerals without the added calories found in animal products.
Environmental Impact

Vegetarian diets have a significantly lower environmental impact compared to meat-based diets. Plant-based food production requires less land, water, and energy, resulting in reduced greenhouse gas emissions and land use.
Greenhouse Gas Emissions
Animal agriculture is a major contributor to greenhouse gas emissions, particularly methane and nitrous oxide. Methane is released from the digestive systems of ruminant animals like cows and sheep, while nitrous oxide is produced from manure management and fertilizer application.
Vegetarian diets eliminate or significantly reduce these emissions by excluding animal products from consumption.
Social and Cultural Aspects
Vegetarianism is a dietary choice that extends beyond personal nutrition; it encompasses social and cultural dimensions. Individuals adopt vegetarianism for various reasons, including ethical concerns, religious beliefs, and personal values.
Ethical Motivations
Many vegetarians choose this lifestyle due to ethical concerns about animal welfare. They believe that animals deserve respect and should not be subjected to suffering or exploitation for human consumption. The ethical perspective extends to the environmental impact of animal agriculture, which contributes to greenhouse gas emissions, deforestation, and water pollution.
Last Word
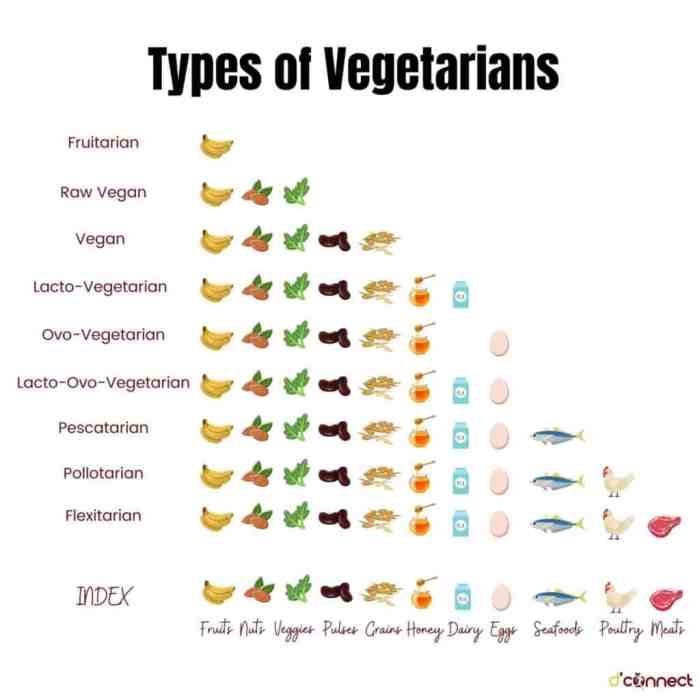
In conclusion, the different types of vegetarian diets provide a diverse range of options for individuals seeking to reduce their meat consumption. Whether driven by health, environmental, or ethical concerns, vegetarianism offers a path towards a more sustainable and compassionate lifestyle.
By carefully considering the nutritional implications and making informed choices, individuals can reap the benefits of a plant-based diet while ensuring they meet their nutritional needs.
FAQ Explained: Different Types Of Vegetarian Diets
What are the main types of vegetarian diets?
The main types of vegetarian diets include lacto-vegetarian (consumes dairy products), ovo-vegetarian (consumes eggs), lacto-ovo vegetarian (consumes both dairy products and eggs), and vegan (excludes all animal products).
What are the nutritional considerations for vegetarian diets?
Vegetarian diets require careful planning to ensure adequate intake of protein, iron, calcium, and vitamin B12. Plant-based sources of these nutrients include legumes, leafy green vegetables, fortified foods, and supplements.
What are the potential health benefits of vegetarian diets?
Vegetarian diets have been associated with a reduced risk of chronic diseases such as heart disease, stroke, type 2 diabetes, and certain types of cancer. They may also promote weight management and improve overall health.
What is the environmental impact of vegetarian diets?
Vegetarian diets have a lower environmental impact compared to meat-based diets. They contribute to reduced greenhouse gas emissions, land use, and water consumption.