What is af in medical terms – Embark on an enlightening journey to unravel the enigmatic world of medical abbreviations. In this comprehensive guide, we decipher the meaning of AF in medical terms, exploring its significance in various medical specialties and providing a roadmap to understanding its usage in clinical settings.
AF, an abbreviation that stands tall in the medical lexicon, serves as a versatile tool for healthcare professionals to communicate efficiently. Whether in assessing fluid balance, evaluating lung function, or diagnosing cardiovascular disorders, AF plays a crucial role in the medical decision-making process.
Delve into the intricacies of AF and unlock the secrets it holds.
Definition of AF in Medical Terms
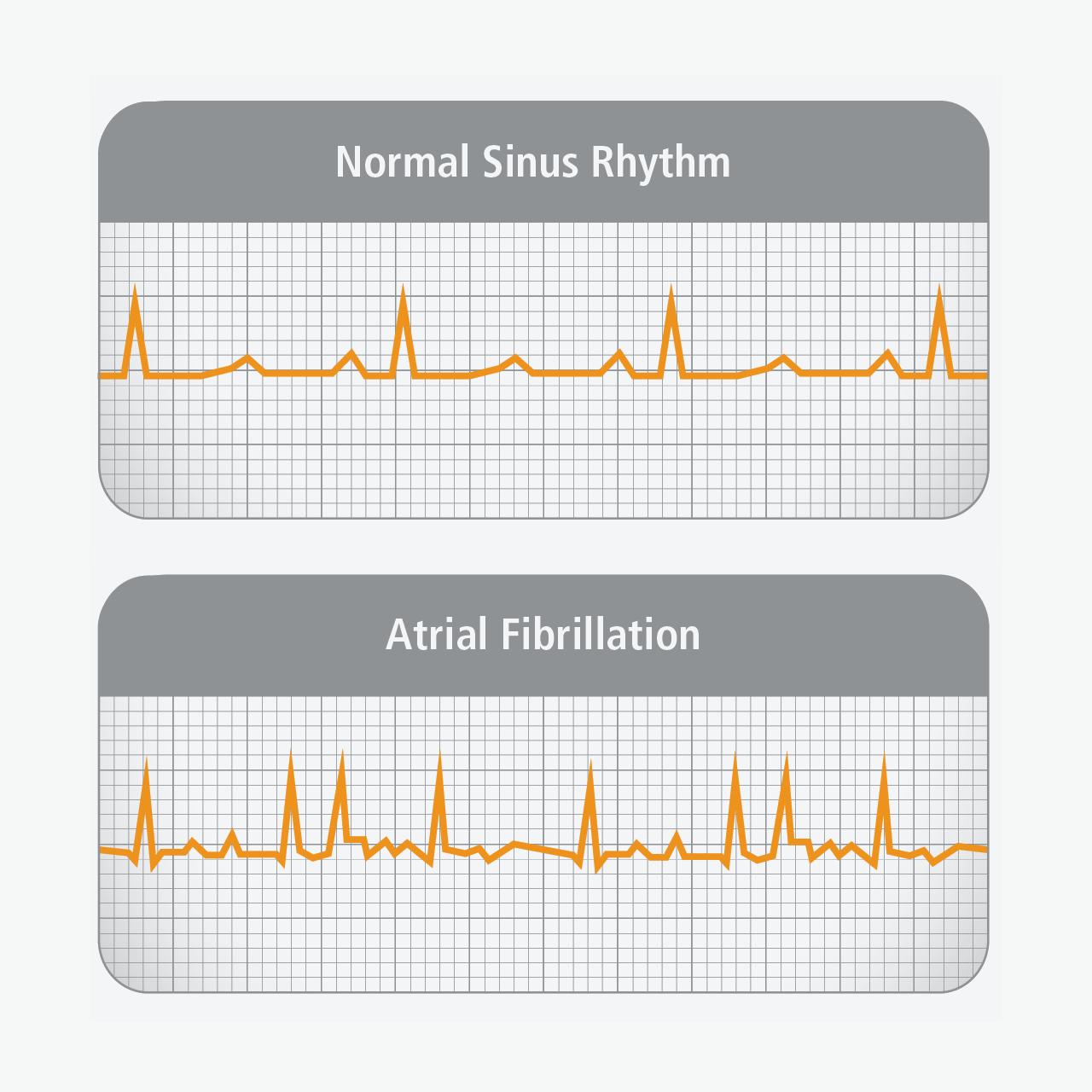
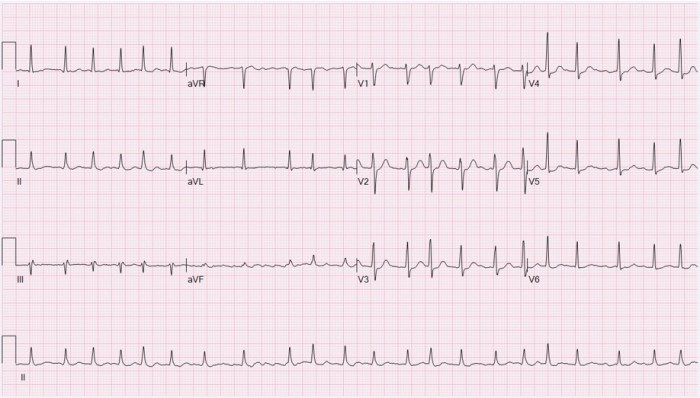
AF is a common abbreviation used in medical terminology to represent “atrial fibrillation.” It is a heart rhythm disorder characterized by irregular and rapid heartbeats that originate in the atria, the upper chambers of the heart.
Examples of AF Usage, What is af in medical terms
AF is frequently encountered in medical records and contexts, such as:
- Patient charts: “Patient presents with paroxysmal AF, characterized by intermittent episodes of irregular heart rhythm.”
- Medication prescriptions: “Digoxin 0.25 mg daily for management of AF.”
- Medical research articles: “AF is a major risk factor for stroke and heart failure.”
AF as a Measurement of Fluid Balance

AF plays a crucial role in assessing the balance of fluids within the body. It reflects the balance between the amount of fluid taken in and the amount excreted. Maintaining proper fluid balance is essential for optimal bodily function and overall health.
In clinical settings, AF is measured through a blood test. The normal range for AF is typically between 135 and 145 mEq/L. When AF levels fall below 135 mEq/L, it indicates a state of hyponatremia, which can result from excessive fluid intake or inadequate salt intake.
Conversely, AF levels above 145 mEq/L indicate hypernatremia, which can occur due to dehydration or excessive salt intake.
Interpretation of AF Results
- Hyponatremia (AF < 135 mEq/L):This condition can lead to symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, headache, and confusion. It can also result in seizures or coma in severe cases.
- Hypernatremia (AF > 145 mEq/L):This condition can cause symptoms such as thirst, fatigue, muscle weakness, and seizures. It can also lead to coma in extreme cases.
AF in Cardiovascular Medicine
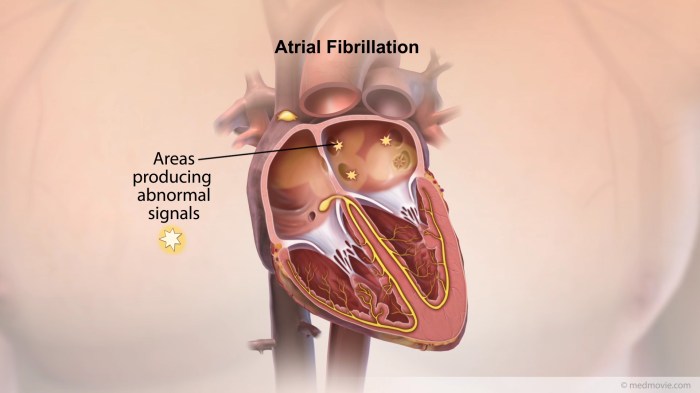
AF plays a crucial role in cardiovascular medicine as it provides valuable insights into the function of the heart and helps identify cardiovascular disorders. It is a non-invasive technique that allows clinicians to assess various aspects of heart function, including its size, shape, and the thickness of its walls.
By analyzing AF images, doctors can identify abnormalities in the heart’s structure and function, which may indicate underlying cardiovascular conditions.
Echocardiography for Heart Function Assessment
Echocardiography is commonly used to assess heart function and diagnose various cardiovascular disorders, such as:
- Valvular heart disease, where the heart valves do not function properly, leading to abnormal blood flow.
- Congenital heart defects, which are structural abnormalities of the heart present from birth.
- Cardiomyopathy, a condition where the heart muscle is weakened or enlarged, affecting its ability to pump blood effectively.
Related Terms and Abbreviations
In the medical context, AF is often associated with several related terms and abbreviations that help healthcare professionals communicate effectively and accurately. Understanding these terms is crucial for comprehending the broader context of AF in medical practice.
The following table provides a list of commonly encountered related terms and abbreviations along with their explanations:
Term
- Atrial Flutter (AFL): A type of abnormal heart rhythm that originates in the atria (upper chambers of the heart) and causes rapid and irregular heartbeats.
- Atrial Tachycardia (AT): Another type of abnormal heart rhythm that originates in the atria, characterized by a rapid and regular heart rate.
- Cardioversion: A medical procedure that involves delivering an electrical shock to the heart to restore a normal heart rhythm.
- Electrocardiogram (ECG): A diagnostic test that records the electrical activity of the heart, providing valuable information for detecting and diagnosing AF.
- Paroxysmal AF: A type of AF that occurs in episodes, with periods of normal heart rhythm in between.
- Persistent AF: A type of AF that lasts for more than seven days.
- Stroke Volume: The amount of blood pumped out of the heart per beat.
- Ventricular Rate (VR): The rate at which the ventricles (lower chambers of the heart) contract.
Last Recap: What Is Af In Medical Terms
In conclusion, AF stands as a multifaceted abbreviation in medical terminology, serving as a valuable tool in a wide range of medical specialties. Its ability to convey complex medical concepts succinctly and accurately makes it an indispensable element in healthcare communication.
Understanding the nuances of AF empowers individuals to engage effectively with healthcare professionals and actively participate in their own health management.
Q&A
What does AF stand for in medical terms?
AF commonly stands for “atrial fibrillation,” a heart condition characterized by an irregular and often rapid heart rate.
How is AF used to assess fluid balance?
AF, or “alveolar fluid,” is a measure of fluid accumulation in the lungs and can indicate fluid overload or imbalances in the body.
What role does AF play in respiratory medicine?
AF is crucial in evaluating lung function, detecting respiratory conditions like pulmonary edema, and assessing the effectiveness of respiratory treatments.
How is AF utilized in cardiovascular medicine?
AF, or “atrial flutter,” is a heart rhythm disorder characterized by rapid and regular heartbeats, and it can be used to diagnose and monitor cardiovascular conditions.